Money (Деньги)
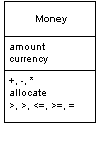
Паттерн проектирования Money
Описание Money
Огромное количество компьютеров в мире обрабатывают данные о деньгах. Удивительно, что класс Деньги до сих пор не является базовым в любом языке программирования. Недостаток такого рода типа данных приводит к проблемам, наиболее заметные из которых - работа с валютой. Если все вычисления в программе проделываются в одной валюте, никаких особых проблем нет, но как только вводится многовалютность - надо думать о том, чтобы не сложить 10 долларов с 10 йенами без перевода курсов валют. Менее заметна проблема с округлением. Денежные вычисления часто округляют до наименьшей из существующих мер. При этом легко не учесть копейки из-за ошибок округления.
Что действительно хорошо в ООП, так это то, что вы можете исправить эти проблемы, созданием класса Money (Деньги), чтобы работать с денежными величинами и избегать общих ошибок.
Примеры реализации
// Money Pattern in JavaScript
class Money {
constructor(amount, currency) {
// Store amount in cents to avoid floating point errors
this.cents = Math.round(amount * 100);
this.currency = currency;
}
get amount() {
return this.cents / 100;
}
equals(other) {
return other instanceof Money &&
this.cents === other.cents &&
this.currency === other.currency;
}
add(other) {
if (this.currency !== other.currency) {
throw new Error(`Cannot add ${this.currency} and ${other.currency}`);
}
return new Money((this.cents + other.cents) / 100, this.currency);
}
subtract(other) {
if (this.currency !== other.currency) {
throw new Error(`Cannot subtract ${this.currency} and ${other.currency}`);
}
return new Money((this.cents - other.cents) / 100, this.currency);
}
multiply(factor) {
return new Money((this.cents * factor) / 100, this.currency);
}
divide(divisor) {
if (divisor === 0) {
throw new Error('Cannot divide by zero');
}
return new Money((this.cents / divisor) / 100, this.currency);
}
isZero() {
return this.cents === 0;
}
isNegative() {
return this.cents < 0;
}
toString() {
return `${this.amount.toFixed(2)} ${this.currency}`;
}
static zero(currency) {
return new Money(0, currency);
}
}
// Usage
const price1 = new Money(19.99, 'USD');
const price2 = new Money(5.01, 'USD');
const total = price1.add(price2);
console.log(total.toString()); // 25.00 USD
const discount = total.multiply(0.1);
const finalPrice = total.subtract(discount);
console.log(finalPrice.toString()); // 22.50 USD// Money Pattern in C++
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
class Money {
private:
long cents;
std::string currency;
public:
Money(double amount, const std::string& currency)
: cents(static_cast<long>(amount * 100)), currency(currency) {}
double getAmount() const {
return static_cast<double>(cents) / 100.0;
}
std::string getCurrency() const {
return currency;
}
bool equals(const Money& other) const {
return cents == other.cents && currency == other.currency;
}
Money add(const Money& other) const {
if (currency != other.currency) {
throw std::runtime_error("Cannot add different currencies");
}
return Money((cents + other.cents) / 100.0, currency);
}
Money subtract(const Money& other) const {
if (currency != other.currency) {
throw std::runtime_error("Cannot subtract different currencies");
}
return Money((cents - other.cents) / 100.0, currency);
}
Money multiply(double factor) const {
return Money((cents * factor) / 100.0, currency);
}
Money divide(double divisor) const {
if (divisor == 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("Cannot divide by zero");
}
return Money((cents / divisor) / 100.0, currency);
}
bool isZero() const {
return cents == 0;
}
bool isNegative() const {
return cents < 0;
}
std::string toString() const {
return std::to_string(getAmount()) + " " + currency;
}
static Money zero(const std::string& currency) {
return Money(0.0, currency);
}
};
// Usage
int main() {
Money price1(19.99, "USD");
Money price2(5.01, "USD");
Money total = price1.add(price2);
std::cout << total.toString() << std::endl; // 25.00 USD
Money discount = total.multiply(0.1);
Money finalPrice = total.subtract(discount);
std::cout << finalPrice.toString() << std::endl; // 22.50 USD
return 0;
}// Money Pattern in Go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
type Money struct {
cents int64
currency string
}
func NewMoney(amount float64, currency string) Money {
return Money{
cents: int64(math.Round(amount * 100)),
currency: currency,
}
}
func (m Money) Amount() float64 {
return float64(m.cents) / 100.0
}
func (m Money) Currency() string {
return m.currency
}
func (m Money) Equals(other Money) bool {
return m.cents == other.cents && m.currency == other.currency
}
func (m Money) Add(other Money) (Money, error) {
if m.currency != other.currency {
return Money{}, fmt.Errorf("cannot add different currencies")
}
return Money{
cents: m.cents + other.cents,
currency: m.currency,
}, nil
}
func (m Money) Subtract(other Money) (Money, error) {
if m.currency != other.currency {
return Money{}, fmt.Errorf("cannot subtract different currencies")
}
return Money{
cents: m.cents - other.cents,
currency: m.currency,
}, nil
}
func (m Money) Multiply(factor float64) Money {
return Money{
cents: int64(math.Round(float64(m.cents) * factor)),
currency: m.currency,
}
}
func (m Money) Divide(divisor float64) (Money, error) {
if divisor == 0 {
return Money{}, fmt.Errorf("cannot divide by zero")
}
return Money{
cents: int64(math.Round(float64(m.cents) / divisor)),
currency: m.currency,
}, nil
}
func (m Money) IsZero() bool {
return m.cents == 0
}
func (m Money) IsNegative() bool {
return m.cents < 0
}
func (m Money) String() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%.2f %s", m.Amount(), m.currency)
}
func ZeroMoney(currency string) Money {
return Money{cents: 0, currency: currency}
}
// Usage
func main() {
price1 := NewMoney(19.99, "USD")
price2 := NewMoney(5.01, "USD")
total, _ := price1.Add(price2)
fmt.Println(total.String()) // 25.00 USD
discount := total.Multiply(0.1)
finalPrice, _ := total.Subtract(discount)
fmt.Println(finalPrice.String()) // 22.50 USD
}# Money Pattern in Python
from decimal import Decimal, ROUND_HALF_UP
from typing import Union
class Money:
def __init__(self, amount: Union[float, Decimal], currency: str):
# Use Decimal for precise decimal arithmetic
self.amount = Decimal(str(amount)).quantize(Decimal('0.01'), rounding=ROUND_HALF_UP)
self.currency = currency
def __add__(self, other: 'Money') -> 'Money':
if self.currency != other.currency:
raise ValueError(f"Cannot add {self.currency} and {other.currency}")
return Money(self.amount + other.amount, self.currency)
def __sub__(self, other: 'Money') -> 'Money':
if self.currency != other.currency:
raise ValueError(f"Cannot subtract {self.currency} and {other.currency}")
return Money(self.amount - other.amount, self.currency)
def __mul__(self, factor: Union[float, Decimal]) -> 'Money':
return Money(self.amount * Decimal(str(factor)), self.currency)
def __truediv__(self, divisor: Union[float, Decimal]) -> 'Money':
if divisor == 0:
raise ValueError("Cannot divide by zero")
return Money(self.amount / Decimal(str(divisor)), self.currency)
def __eq__(self, other: 'Money') -> bool:
return self.amount == other.amount and self.currency == other.currency
def __str__(self) -> str:
return f"{self.amount} {self.currency}"
def is_zero(self) -> bool:
return self.amount == 0
def is_negative(self) -> bool:
return self.amount < 0
@classmethod
def zero(cls, currency: str) -> 'Money':
return cls(0, currency)
# Usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
price1 = Money(19.99, "USD")
price2 = Money(5.01, "USD")
total = price1 + price2
print(total) # 25.00 USD
discount = total * 0.1
final_price = total - discount
print(final_price) # 22.50 USD<?php
// Money Pattern in PHP
class Money {
private $amount;
private $currency;
public function __construct($amount, $currency) {
// Use BC Math for precise decimal arithmetic
$this->amount = bcadd($amount, '0', 2);
$this->currency = $currency;
}
public function getAmount() {
return $this->amount;
}
public function getCurrency() {
return $this->currency;
}
public function equals(Money $other) {
return bccomp($this->amount, $other->amount, 2) === 0 &&
$this->currency === $other->currency;
}
public function add(Money $other) {
if ($this->currency !== $other->currency) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException("Cannot add different currencies");
}
return new Money(bcadd($this->amount, $other->amount, 2), $this->currency);
}
public function subtract(Money $other) {
if ($this->currency !== $other->currency) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException("Cannot subtract different currencies");
}
return new Money(bcsub($this->amount, $other->amount, 2), $this->currency);
}
public function multiply($factor) {
return new Money(bcmul($this->amount, $factor, 2), $this->currency);
}
public function divide($divisor) {
if ($divisor == 0) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException("Cannot divide by zero");
}
return new Money(bcdiv($this->amount, $divisor, 2), $this->currency);
}
public function isZero() {
return bccomp($this->amount, '0', 2) === 0;
}
public function isNegative() {
return bccomp($this->amount, '0', 2) < 0;
}
public function __toString() {
return $this->amount . " " . $this->currency;
}
public static function zero($currency) {
return new Money('0', $currency);
}
}
// Usage
$price1 = new Money('19.99', 'USD');
$price2 = new Money('5.01', 'USD');
$total = $price1->add($price2);
echo $total . "\n"; // 25.00 USD
$discount = $total->multiply('0.1');
$finalPrice = $total->subtract($discount);
echo $finalPrice . "\n"; // 22.50 USD
?>Использована иллюстрация с сайта Мартина Фаулера.